What is asthma?
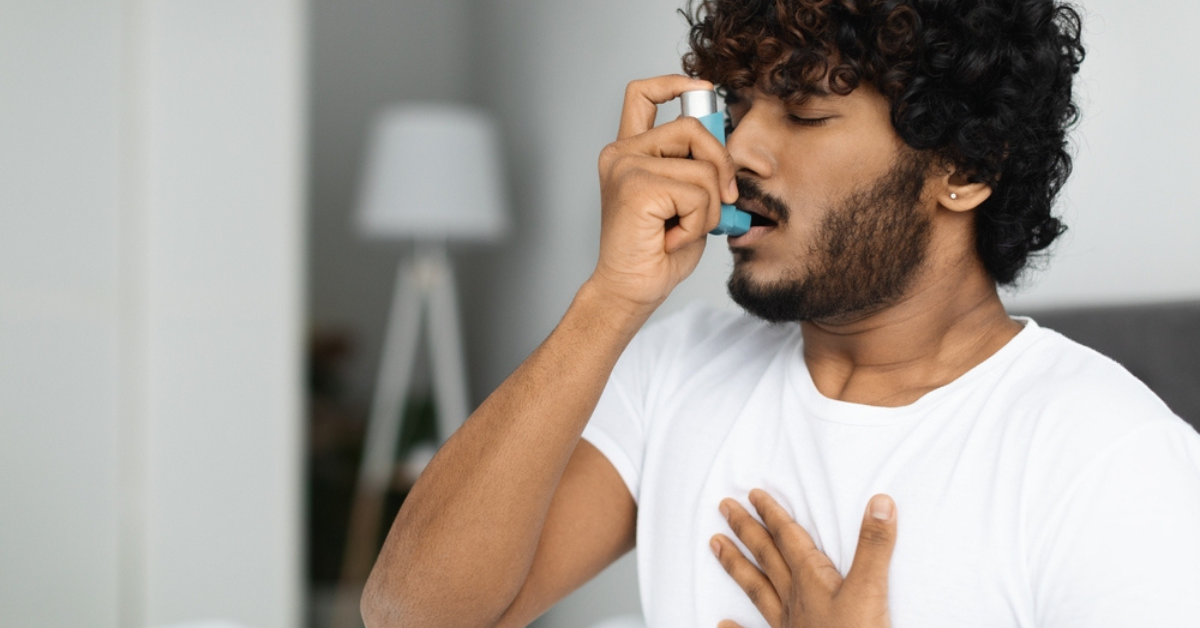
Many individuals around the world struggle with the chronic respiratory disease known as asthma. It causes symptoms like wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and tightness in the chest and is characterized by inflammation and constriction of the airways. While asthma cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.
Common symptoms of asthma
Recognizing the symptoms of asthma is crucial for early diagnosis and proper management. The most common symptoms include
- Wheezing, a whistling sound when breathing
- Coughing, especially at night or during exercise
- Shortness of breath, feeling out of breath or unable to take deep breaths
- Chest tightness, a squeezing sensation in the chest
These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency from person to person, and they may worsen during asthma attacks or when exposed to triggers.
Asthma Triggers and Prevention
There are many different things that might cause asthma symptoms. Common triggers include allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold; irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and strong odors; respiratory infections like colds and flu; physical exertion and exercise; and emotional stress. Avoiding or minimizing exposure to these triggers is essential in preventing asthma attacks. This can be achieved by maintaining a clean and dust-free environment, avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, practicing good hygiene, and managing stress levels.
Types of asthma treatment
Asthma treatment aims to control symptoms, prevent asthma attacks, and improve overall lung function. The treatment plan may vary depending on the severity and frequency of symptoms. The two major approaches to treating asthma are drugs for long-term control and treatments for acute relief.
Long-term control medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting beta-agonists, are taken regularly to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms.
Quick-relief medications, such as short-acting beta-agonists, provide immediate relief during asthma attacks or when symptoms worsen.
Inhalers and nebulizers: Understanding breathing treatment for asthma
Inhalers and nebulizers are commonly used devices for delivering asthma medications directly to the airways. Inhalers are portable handheld devices that deliver medication in the form of a fine mist or powder, which is inhaled through the mouth. Nebulizers, on the other hand, are larger machines that convert liquid medication into a fine mist, which is inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece. Both inhalers and nebulizers are effective in delivering medication directly to the lungs, providing quick breathing treatment for asthma
Medications for asthma management
Along with inhalers and nebulizers, there are various medications available for asthma management. In addition to long-term control medications and quick-relief medications, other medications may be prescribed based on individual needs.
These may include oral corticosteroids for severe asthma flare-ups, immunomodulators to reduce allergic reactions, and monoclonal antibodies to target specific molecules involved in asthma inflammation. It is important to work closely with an asthma specialist or healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medications and dosage for optimal management.
Lifestyle changes for asthma management
In addition to medications, certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve asthma management. First and foremost, it is essential to identify and avoid triggers that worsen asthma symptoms. This may involve creating a dust-free environment, using hypoallergenic bedding, keeping pets out of the bedroom, and implementing proper ventilation.
Regular exercise is also important for overall lung health, but it is crucial to choose activities that do not trigger asthma symptoms. It may be helpful to warm up before exercising, use a bronchodilator inhaler before physical activity, and monitor symptoms during exercise. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep can all contribute to better asthma control.
Asthma and exercise: Tips for staying active
Having asthma does not mean giving up on physical activity. In fact, regular exercise can strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve lung function. However, it is important to take certain precautions to minimize the risk of triggering asthma symptoms during exercise.
Before starting any exercise program, consult with an asthma specialist or healthcare provider to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your condition. It may be helpful to warm up before exercising, wear a scarf or mask in cold weather, avoid exercising in polluted environments, and always carry a quick-relief inhaler. Monitoring your symptoms during exercise and adjusting the intensity or duration of your workout accordingly can also help you stay active while managing your asthma effectively.
Conclusion
Living with asthma requires diligent management and a proactive approach to treatment. Individuals with asthma can breathe easy and lead a fulfilling life by understanding the nature of asthma, recognizing common symptoms, identifying triggers, and following an appropriate treatment plan.
It is important to work closely with an asthma specialist or healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your specific needs. Remember, asthma can be effectively managed, allowing you to enjoy a life free from the limitations imposed by this chronic respiratory condition.
If you or a loved one is living with asthma, consult an asthma specialist for personalized treatment and management strategies. Breathe easily by taking charge of your respiratory health.








0 Comments